Recombinant Mouse Eyes absent homolog 1 (Eya1)
-
中文名称:小鼠Eya1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP007906MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Eya1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP007906MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Eya1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP007906MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Eya1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP007906MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Eya1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP007906MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Eya1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Eya1; Eyes absent homolog 1; EC 3.1.3.16; EC 3.1.3.48
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-591
-
氨基酸序列MEMQDLTSPH SRLSGSSESP SGPKLDSSHI NSTSMTPNGT EVKTEPMSSS EIASTAADGS LDSFSGSALG SSSFSPRPAH PFSPPQIYPS KSYPHILPTP SSQTMAAYGQ TQFTTGMQQA TAYATYPQPG QPYGISSYGA LWAGIKTESG LSQSQSPGQT GFLSYGTSFG TPQPGQAPYS YQMQGSSFTT SSGLYSGNNS LTNSSGFNSS QQDYPSYPGF GQGQYAQYYN SSPYPAHYMT SSNTSPTTPS TNATYQLQEP PSGVTSQAVT DPTAEYSTIH SPSTPIKETD SERLRRGSDG KSRGRGRRNN NPSPPPDSDL ERVFIWDLDE TIIVFHSLLT GSYANRYGRD PPTSVSLGLR MEEMIFNLAD THLFFNDLEE CDQVHIDDVS SDDNGQDLST YNFGTDGFPA AATSANLCLA TGVRGGVDWM RKLAFRYRRV KEIYNTYKNN VGGLLGPAKR EAWLQLRAEI EALTDSWLTL ALKALSLIHS RTNCVNILVT TTQLIPALAK VLLYGLGIVF PIENIYSATK IGKESCFERI IQRFGRKVVY VVIGDGVEEE QGAKKHAMPF WRVSSHSDLM ALHHALELEY L
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Functions both as protein phosphatase and as transcriptional coactivator for SIX1, and probably also for SIX2, SIX4 and SIX5. Tyrosine phosphatase that dephosphorylates 'Tyr-142' of histone H2AX (H2AXY142ph) and promotes efficient DNA repair via the recruitment of DNA repair complexes containing MDC1. 'Tyr-142' phosphorylation of histone H2AX plays a central role in DNA repair and acts as a mark that distinguishes between apoptotic and repair responses to genotoxic stress. Its function as histone phosphatase may contribute to its function in transcription regulation during organogenesis. Has also phosphatase activity with proteins phosphorylated on Ser and Thr residues (in vitro). Required for normal embryonic development of the craniofacial and trunk skeleton, kidneys and ears. Together with SIX1, it plays an important role in hypaxial muscle development; in this it is functionally redundant with EYA2.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Notch is regulated by the threonine phosphatase activity of Eya1. Eya1 dephosphorylates p-threonine-2122 of the Notch1 intracellular domain (Notch1 ICD), which increases the stability of Notch1 ICD and maintains Notch signaling activity in the non-neuronal epibranchial placodal cells. PMID: 29140246
- data support a model where Eya-Six may form a complex to regulate nephron progenitor cell development before metanephric specification and are critical mesenchymal factors for inducing nephric duct development. PMID: 25903664
- Eya1 phosphatase promotes Shh signaling during hindbrain development and oncogenesis PMID: 25816987
- results reveal a functional link between Eya1, Six2, and Myc in driving the expansion and maintenance of the multipotent progenitors during nephrogenesis PMID: 25458011
- BOR syndrome-associated Eya1 missense mutations S454P, L472R, and L550P lead to enhanced proteasomal degradation of the Eya1 protein. PMID: 24489909
- these findings reveal that the canonical Wnt and PI3K/Akt signal pathways restrain the GSK3/Fbw7-dependent Eya1 ubiquitination, and they further suggest that dysregulation of this novel axis contributes to tumorigenesis. PMID: 24752894
- The EYA1 phosphatase regulates cell-cycle control via transcriptional complex formation at the cyclin D1 promoter. PMID: 23636126
- These findings uncover novel functions for Six1-Eya1-SHH pathway during the saccular phase of lung morphogenesis. PMID: 23895934
- EYA1 is efficiently degraded during mitotic exit in a ANAPC1-dependent manner and these two proteins physically interact. PMID: 23263983
- EYA1 and SIX1 drive the neuronal developmental program in cooperation with the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex and SOX2 in the mammalian inner ear. PMID: 22513373
- Deletion of either or both Six1 and Eya1 genes results in genitourinary tract defects including persistent cloaca; hypospadias; and hypoplastic genitalia. PMID: 21968101
- Six1 and Eya1 genetically interacted with Fgf8 and the Tbx1 pathway that is crucial for cardiovascular and craniofacial morphogenesis PMID: 21364285
- Eya1 function is critical for proper coordination of lung epithelial, mesenchymal and vascular development. PMID: 21129374
- Data report the identification of the related proteins Sipl1 (Shank-interacting protein-like 1) and Rbck1 (RBCC protein interacting with PKC1) as novel interaction partners of Eya1. PMID: 20956555
- Eya1 IS required for normal ear develoPMENT PMID: 11804780
- Impaired interactions between mouse Eyal harboring mutations found in patients with branchio-oto-renal syndrome and Six, Dach, and G proteins PMID: 11950062
- Eya1 is required for the morphogenesis of mouse thymus, parathyroid and thyroid. PMID: 12070080
- Data identify Six1 and Eya1 as the first transcriptional complex that is able to reprogram adult slow-twitch oxidative fibers toward a fast-twitch glycolytic phenotype. PMID: 15226428
- constructs of the homologous region ( Eya1HR and Eya4HR) interact with Six1 prey constructs, although no interaction with Dach1 prey was demonstrable PMID: 15492887
- During the development of epibranchial placode-derived distal cranial sensory ganglia, while the phenotype appears less severe in Six1 than in Eya1 mutants PMID: 15496442
- Eya1 signaling is critical to the normal expression patterns of Tbx1, Ngn1, and NeuroD in the developing mouse otocyst PMID: 15817220
- Eya1 acts as a critical regulator for specifying the metanephric mesenchyme. PMID: 16018995
- essential role for Eya1 and Six genes in patterning the third pouch into organ-specific primordia PMID: 16530750
- Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR)-associated mutations lead to a loss of phosphatase activity in Eya1 proteins, while mutations associated with ocular defects yield Eya1 proteins with near normal levels of phosphatase activity. PMID: 16797546
- These results show that, while Eya1 exerts an early function essential for normal growth and patterning of the otic epithelium, it also functionally synergizes with Pax2 during the morphogenesis of all sensory areas of mammalian inner ear. PMID: 16916509
- Eya1 protein is required for hypaxial somitic myogenesis in the mouse embryo PMID: 17098221
- Eya1 activity, in a concentration-dependent manner, plays a key role in the regulation of genes known to be important for sensory development PMID: 18678597
- phosphatase activity of a number of variants of the mouse Eya1 protein that harbours single point mutations that were associated with branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR), branchio-oto syndrome (BO) and ocular defects, respectively, in humans PMID: 18759246
- a comprehensive group of enhancers around Eya1 locus, which are probably involved in the control of the complex expression pattern of Eya1 in vivo. PMID: 18816442
- Mapping of genetic modifiers of Eya1 ( bor/bor ) in CAST/EiJ and BALB/cJ that suppress cochlear aplasia and associated deafness. PMID: 18836772
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:A spontaneous mutation leading to decreased Eya1 expression gives rise to the Eya1-bor phenotype. It is characterized by circling behavior and deafness, due to gross morphological abnormalities of the inner ear, and dysmorphic or missing kidneys. This autosomal recessive trait resembles human branchio-oto-renal (BOR) syndrome.
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:HAD-like hydrolase superfamily, EYA family
-
组织特异性:Extensively expressed in cranial placodes, branchial arches, CNS and developing eye and nose.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14048
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000126383
UniGene: Mm.250185
Most popular with customers
-
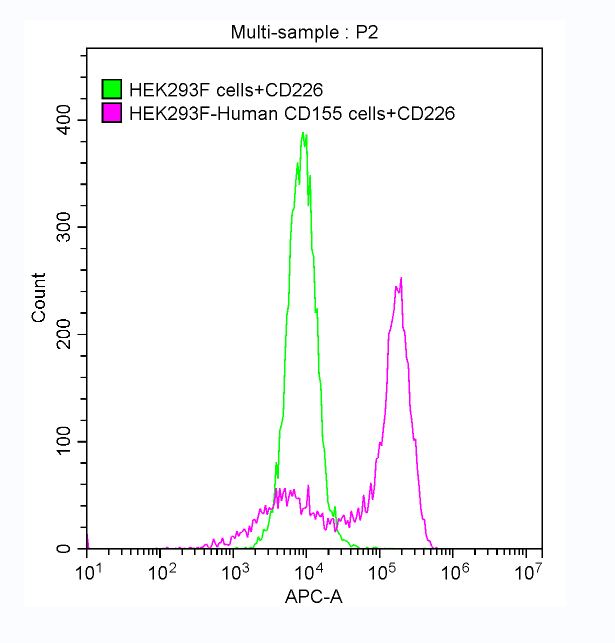
Recombinant Human CD226 antigen (CD226), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
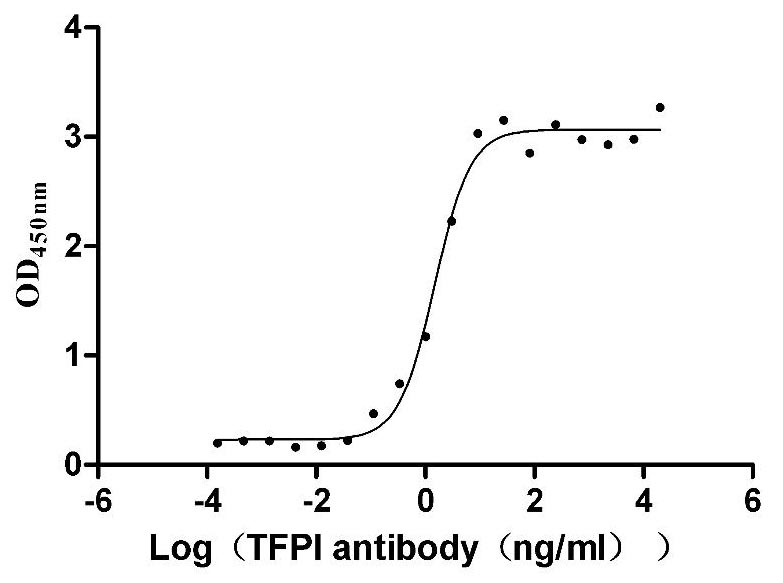
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
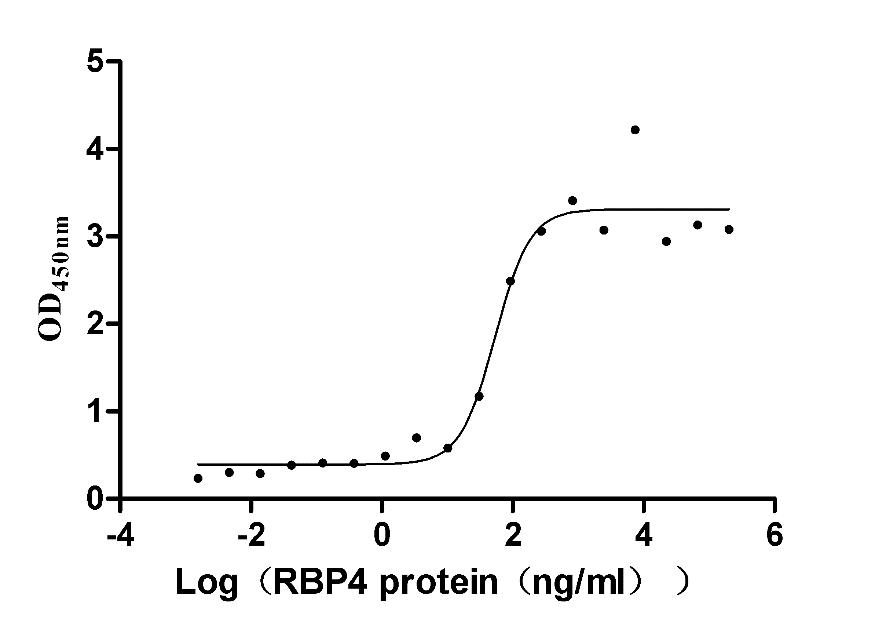
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD93 molecule (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
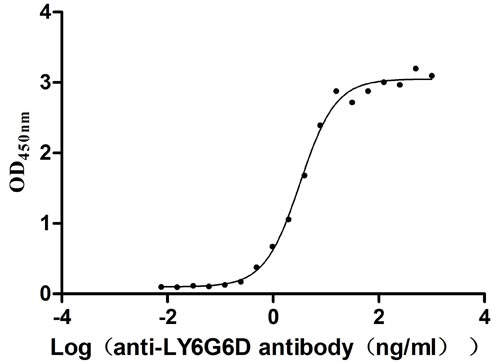
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
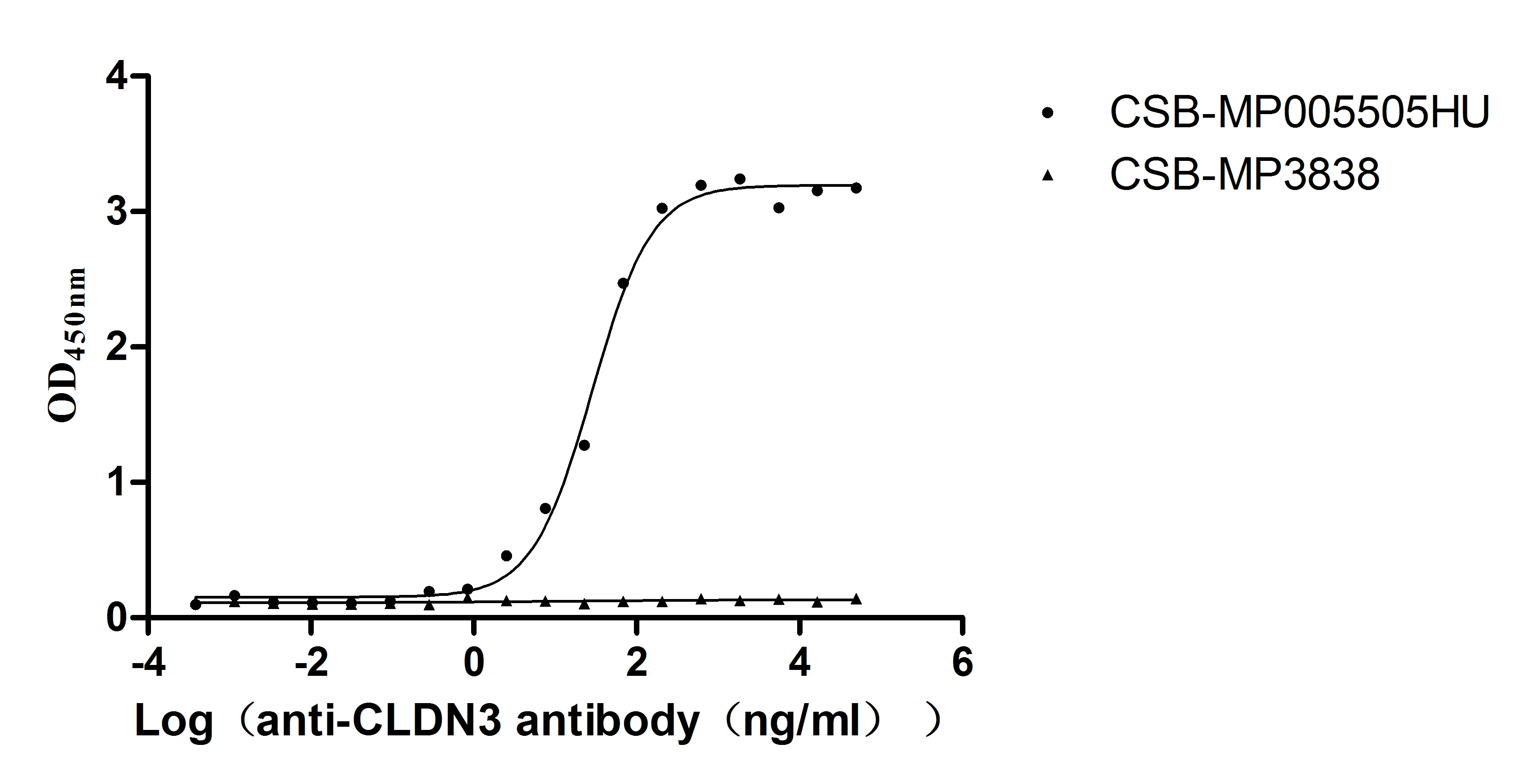
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)